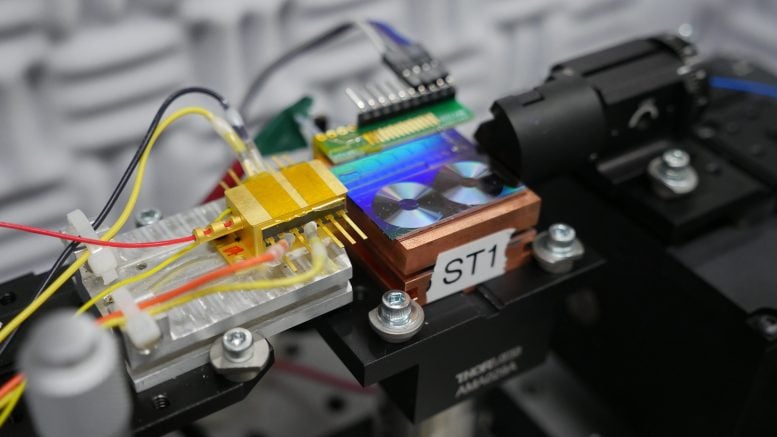
NIST researchers test a chip for converting light into microwave signals. Pictured is the chip, which is the fluorescent panel that looks like two tiny vinyl records. The gold box to the left of the chip is the semiconductor laser that emits light to the chip. Credit: K. Palubicki/NIST
Compact chips enhance precision timing for communication, navigation, and various applications.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and its collaborators have delivered a small but mighty advancement in timing technology: compact chips that seamlessly convert light into microwaves. This chip could improve <span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]” tabindex=”0″ role=”link”>GPS, the quality of phone and internet connections, the <span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]” tabindex=”0″ role=”link”>accuracy of radar and sensing systems, and other technologies that rely on high-precision timing and communication.
This technology reduces something known as timing jitter, which is small, random changes in the timing of microwave signals. Similar to when a musician is trying to keep a steady beat in music, the timing of these signals can sometimes waver a bit. The researchers have reduced these timing wavers to a very small fraction of a second — 15 femtoseconds to be exact, a big improvement over traditional microwave sources — making the signals much more stable and precise in ways that could increase radar sensitivity, the accuracy of analog-to-digital converters and the clarity of astronomical images captured by groups of telescopes.
The team’s results were published in Nature.
Shining a Light on Microwaves
What sets this demonstration apart is the compact design of the components that produce these signals. For the first time, researchers have taken what was once a tabletop-size system and shrunken much of it into a compact chip, about the same size as a digital camera memory card. Reducing timing jitter on a small scale reduces power usage and makes it more usable in everyday devices.
Right now, several of the components for this technology are located outside of the chip, as researchers test their effectiveness. The ultimate goal of this project is to integrate all the different parts, such as lasers, modulators, detectors, and optical amplifiers, onto a single chip.
By integrating all the components onto a single chip, the team could reduce both the size and power consumption of the system. This means it could be easily incorporated into small devices without requiring lots of energy and specialized training.
“The current technology takes several labs and many Ph.D.s to make microwave signals happen,” said Frank Quinlan, NIST physical scientist. “A lot of what this research is about is how we utilize the advantages of optical signals by shrinking the size of components and making everything more accessible.”
To accomplish this, researchers use a semiconductor laser, which acts as a very steady flashlight. They direct the light from the laser into a tiny mirror box called a reference cavity, which is like a miniature room where light bounces around. Inside this cavity, some light frequencies are matched to the size of the cavity so that the peaks and valleys of the light waves fit perfectly between the walls. This causes the light to build up power in those frequencies, which is used to keep the laser’s frequency stable. The stable light is then converted into microwaves using a device called a frequency comb, which changes high-frequency light into lower-pitched microwave signals. These precise microwaves are crucial for technologies like navigation systems, communication networks, and radar because they provide accurate timing and synchronization.
“The goal is to make all these parts work together effectively on a single platform, which would greatly reduce the loss of signals and remove the need for extra technology,” said Quinlan. “Phase one of this project was to show that all these individual pieces work together. Phase two is putting them together on the chip.”
In navigation systems such as GPS, the precise timing of signals is essential for determining location. In communication networks, such as mobile phone and internet systems, accurate timing and synchronization of multiple signals ensure that data is transmitted and received correctly.
For example, synchronizing signals is important for busy cell networks to handle multiple phone calls. This precise alignment of signals in time enables the cell network to organize and manage the transmission and reception of data from multiple devices, like your cellphone. This ensures that multiple phone calls can be carried over the network simultaneously without experiencing significant delays or drops.
In radar, which is used for detecting objects like airplanes and weather patterns, precise timing is crucial for accurately measuring how long it takes for signals to bounce back.
“There are all sorts of applications for this technology. For instance, astronomers who are imaging distant astronomical objects, like black holes, need really low-noise signals and clock synchronization,” said Quinlan. “And this project helps get those low noise signals out of the lab, and into the hands of radar technicians, of astronomers, of environmental scientists, of all these different fields, to increase their sensitivity and ability to measure new things.”
Working Together Toward a Shared Goal
Creating this type of technological advancement is not done alone. Researchers from the University of Colorado Boulder, the <span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]” tabindex=”0″ role=”link”>NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, the University of California Santa Barbara, the University of Virginia, and <span class="glossaryLink" aria-describedby="tt" data-cmtooltip="
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]” tabindex=”0″ role=”link”>Yale University came together to accomplish this shared goal: to revolutionize how we harness light and microwaves for practical applications.
“I like to compare our research to a construction project. There’s a lot of moving parts, and you need to make sure everyone is coordinated so the plumber and electrician are showing up at the right time in the project,” said Quinlan. “We all work together really well to keep things moving forward.”
This collaborative effort underscores the importance of interdisciplinary research in driving technological progress, Quinlan said.
Reference: “Photonic chip-based low-noise microwave oscillator” by Igor Kudelin, William Groman, Qing-Xin Ji, Joel Guo, Megan L. Kelleher, Dahyeon Lee, Takuma Nakamura, Charles A. McLemore, Pedram Shirmohammadi, Samin Hanifi, Haotian Cheng, Naijun Jin, Lue Wu, Samuel Halladay, Yizhi Luo, Zhaowei Dai, Warren Jin, Junwu Bai, Yifan Liu, Wei Zhang, Chao Xiang, Lin Chang, Vladimir Iltchenko, Owen Miller, Andrey Matsko, Steven M. Bowers, Peter T. Rakich, Joe C. Campbell, John E. Bowers, Kerry J. Vahala, Franklyn Quinlan and Scott A. Diddams, 6 March 2024, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07058-z
