A new air-powered computer detects failures in medical devices using air pressure, eliminating electronic sensors for a safer, cheaper alternative. Future plans include expanding its use to hazardous environments.
Researchers have developed an air-powered computer that can detect and issue alerts when certa in medical devices fail. This device simplifies the monitoring process by eliminating the need for electronic sensors, offering a cost-effective and reliable way to help prevent blood clots and strokes.
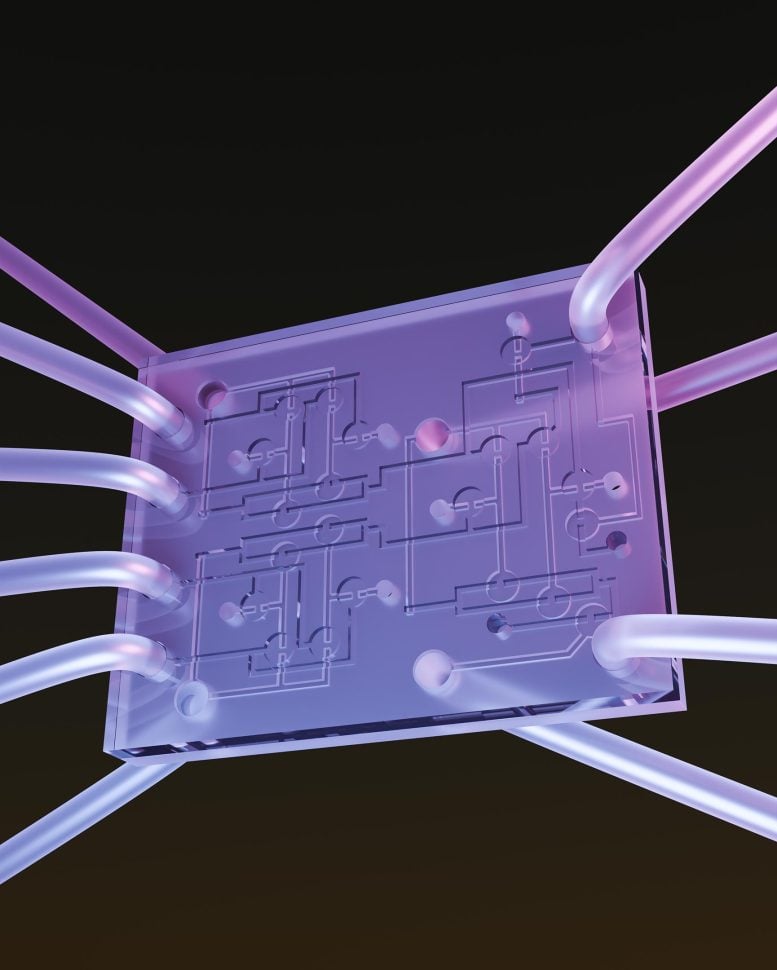
The computer, described in a paper in the journal Device, not only runs on air but also uses air to issue warnings. It immediately blows a whistle when it detects a problem with the lifesaving compression machine it is designed to monitor.
Enhancing Medical Device Safety with Pneumatic Technology
Intermittent pneumatic compression or IPC devices are leg sleeves that fill with air periodically and squeeze a person’s legs to increase blood flow. This prevents clots that lead to blocked blood vessels, strokes, or death. Typically, these machines are powered and monitored by electronics.
“IPC devices can save lives, but all the electronics in them make them expensive. So, we wanted to develop a pneumatic device that gets rid of some of the electronics, to make these devices cheaper and safer,” said William Grover, associate professor of bioengineering at UC Riverside and corresponding paper author.
Technical Insights: How Air-Powered Computers Work
Pneumatics move compressed air from place to place. Emergency brakes on freight trains operate this way, as do bicycle pumps, tire pressure gauges, respirators, and IPC devices. It made sense to Grover and his colleagues to use one pneumatic logic device to control another and make it safer.
This type of device operates in a similar way to electronic circuits, by making parity bit calculations. “Let’s say I want to send a message in ones and zeroes, like 1-0-1, three bits,” Grover said. “Decades ago, people realized they could send these three bits with one additional piece of information to make sure the recipient got the right message.”
That extra piece of information is called a parity bit. The bit is a number — 1 if the message contains an odd number of ones and 0 if the message contains an even number of ones. Should the number one appear at the end of a message with an even number of bits, then it is clear the message was flawed. Many electronic computers send messages this way.
[embedded content]
Demonstration of the pneumatic logic sensor made to detect performance errors in compression devices. Credit: William Grover/UCR
Practical Applications and Future Prospects
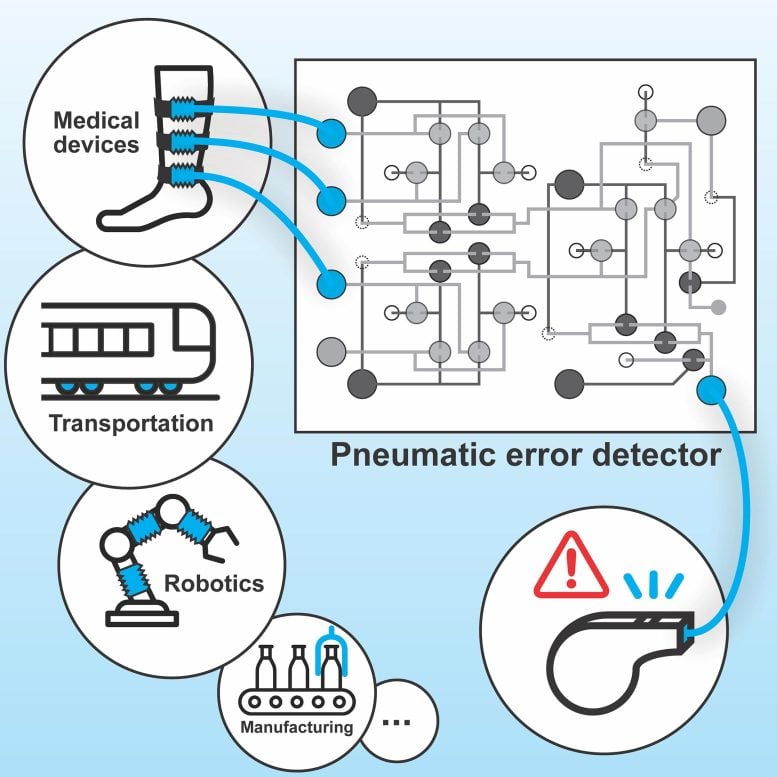
An air-powered computer uses differences in air pressure flowing through 21 tiny valves to count the number of ones and zeroes. If no error in counting has occurred, then the whistle doesn’t blow.
If it does blow, that’s a sign the machine requires repairs. In a video demonstrating the air computer, Grover and his students are shown damaging an IPC device with a knife, rendering it unusable. Seconds later, the whistle blows.
“This device is about the size of a box of matches. It replaces a handful of sensors as well as a computer,” Grover said. “So, we can reduce costs while still detecting problems in a device. And it could also be used in high humidity or high temperature environments that aren’t ideal for electronics.”
The IPC device monitoring is only one application for air computing. For his next project, Grover would like to design a device that could eliminate the need for a job that kills people every year — moving around grain at the top of tall silos.
Tall buildings full of corn or wheat, grain silos are a common sight in the Midwest. Often, a human has to go inside with a shovel to break up the grains and even out the piles inside.
“A remarkable number of deaths occur because the grain shifts and the person gets trapped. A robot could do this job instead of a person. However, these silos are explosive, and a single electric spark could blow a silo apart, so an electronic robot may not be the best choice,” Grover said. “I want to make an air-powered robot that could work in this explosive environment, not generate any sparks, and take humans out of danger.”
Air-powered computing is an idea that has been around for at least a century. People used to make air-powered pianos that could play music from punched rolls of paper. After the rise of modern computing, engineers lost interest in pneumatic circuits.
“Once a new technology becomes dominant, we lose awareness of other solutions to problems,” Grover said. “One thing I like about this research is that it can show the world that there are situations today when 100-plus-year-old ideas can still be useful.”
Reference: “Air-powered logic circuits for error detection in pneumatic systems” by Shane Hoang, Mabel Shehada, Zinal Patel, Minh-Huy Tran, Konstantinos Karydis, Philip Brisk and William H. Grover, 12 August 2024, Device.
DOI: 10.1016/j.device.2024.100507
